Blockchain and Cryptocurrency are new concepts to many people, although this is changing every year now as we edge closer to mainstream adoption.
With every new technology comes the inevitable matrix of new terms, abbreviations, acronyms and concepts that at first can seem overly complex, confusing and overwhelming.
Just picture back to when the World Wide Web had been around for some time, but only just becoming a household term.
Back then everyone would have to have learned what the terms browser, URL, email, HTTP, HTML, Domain Name System (DNS), links, pages, Website, Search engine, and much much more.
However, now the above terms and concepts are second nature to many of us throughout the entire world and are used by almost all businesses on the planet.
This is comparable to where Blockchain and Cryptocurrency are now (2021)!
To help breakdown some terminology barriers we have compiled a glossary below to help explain what many of the common crypto terms, phrases or concepts actually mean.
Blockchain and Cryptocurrency terms
| wdt_ID | Term | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Fiat money (or Fiat Currency) | Government issued currency and is legal tender whose value is backed by the government, or Central bank which issued it. Examples include Australian dollar (AUD), British pound (GBP), Euro, Japanese yen (JPY), South Korean won (KRW), United States Dollar (USD), etc. |
| 2 | Private Key | Cryptocurrency wallet Private Key, made up of letters and numbers, which is used to access your digital assets/cryptocurrency, and should never be disclosed to anyone. There is a saying in the industry that "If You Don't Own Your Private Keys, You Don't Own Your Crypto". I can't stress the importance of this point enough! |
| 4 | Public Key | Cryptocurrency wallet Public Key is an address, made up of letters and numbers, where a person or business can receive digital assets/cryptocurrency. |
| 5 | Wallet (Cryptocurrency wallet) | A Cryptocurrency wallet is a device (physical/hardware, software or a service) which facilitates the sending and receiving of Cryptocurrency and gives ownership by storing vital information such as the private and/or public keys plus owners balance. In addition to this basic function of storing the keys, a Cryptocurrency wallet more often also offers the functionality of encrypting and/or signing information. Signing can for example result in executing a smart contract, a cryptocurrency transaction, identification or legally signing a "document". Source: Wikipedia - Cryptocurrency wallet |
| 6 | White paper | The developers of a Cryptocurrency, normally publish a "White paper" which informs readers concisely about the issue or problem they are looking to solve, presents the issuing body's philosophy on the matter, present comprehensive information on the digital asset and it's underlying technology. White papers are generally meant to present a complex issue into material for the reader to make an informed decision on the need, scope and technology of the project before becoming involved or investing in it. |
| 7 | Token | A Token is a Cryptocurrency which requires another blockchain to operate on, and therefore does not have it's own native blockchain. A Token benefits from the technology of the blockchain it runs on, without the cost, complexities and need to build their own blockchain. Examples include 0x (ZRX), Bancor (BNT), and ERC-20 tokens which run on the Ethereum network. Many crypto projects run as a token before developing and migrating to their own blockchain (mainnet). |
| 8 | Coin | A Coin is a Cryptocurrency which operates it's own native blockchain. Examples of crypto coins include Bitcoin (BTC), Ethereum's Ether (ETH), Polkadot (DOT), Cardano (ADA), Stellar (XLM), EOS (EOS), Tezos (XTZ), etc. |
| 9 | Proof of work (PoW) | PoW is a type of consensus mechanism by which a Cryptocurrency blockchain network achieves distributed consensus. Bitcoin is the largest of all Cryptocurrencies that uses Proof of work. |
| 10 | Proof of stake (PoS) | PoS is a type of consensus mechanism by which a Cryptocurrency blockchain network achieves distributed consensus. |
| 11 | Consensus | Coordinating processes to reach consensus in the blockchain. Consensus algorithms are designed to achieve reliability in a network which may have one or more unreliable nodes. |
| 12 | Blockchain | Blockchain is Distributed ledger technology using cryptography and predefined software rules that make it extremely difficult for attackers to manipulate, and records the provenance of a digital asset, such as Bitcoin. Blockchain is also commonly referred to as a decentralized Distributed ledger, Distributed ledger technology or simply DLT. |
| 13 | Bitcoin (BTC) |
Bitcoin (₿ or "BTC" as it's often referred to) is a new form of currency, a Digital currency called Cryptocurrency, which can be held as a digital asset or exchanged for something you value. Unlike traditional money/currency, it is not controlled by any one government, organization or person. Bitcoin is built and runs on a Blockchain which is a decentralized, distributed ledger. Uses include buying goods & services, speculate on it's price (purchasing power) or be held as a store of value. Please refer to our "What is Bitcoin" definitive guide for a comprehensive explanation of all concepts associated with Bitcoin. |
| 15 | Staking | A way for crypto owners to verify and secure transactions on a blockchain and receive a staking reward (additional Cryptocurrency), deposited at regular intervals, for their contribution to securing the network. You can thing of Staking as potentially a way to earn passive income while holding your Cryptocurrency, however like every financial transaction, there are pros and cons you must understand to see if they suit your personal situation. While there are many Cryptocurrencies that can be staked, including Ethereum 2.0, Polkadot (DOT), Cardano (ADA), Cosmos (ATOM), Tezos (XTZ), not all cryptos can be. Staking Rewards (https://www.stakingrewards.com) is a great resource to find crypto assets that can be staked, the percentage of eligible tokens that are currently staked for each asset, dollar value staked and much more. |
| 16 | Mining | Cryptocurrency mining can be a very complex topic, however the high-level definition is that mining involves the solving of complex encryption and algorithms to verify and add transactions to the blockchain. Miners receive payments, in the Cryptocurrency they are mining, for completing this costly process. The high cost of mining is due to the level of computing hardware required and the large amounts of electricity it uses to solve incredibly complex encryption. |
| 17 | Cryptocurrency exchange | A company (a centralized exchange) or product (such as a decentralized exchange) that allows customers to trade cryptocurrencies or digital currencies for other assets, such as conventional Fiat currency or other digital currencies. |
| 18 | Crypto | A shortened version of the word Cryptocurrency |
| 19 | Decentralization (Decentralized) | In relation to a Blockchain, Decentralization means that the record of transactions on the Blockchain cannot be altered by any one entity (country, organization or individual person) and is therefore classed as being Decentralized. |
| 20 | Nodes | The backbone/infrastructure of a Blockchain. Essentially a Blockchain is stored on it's nodes, which are devices/computers which verify, preserve and distribute data about the Blockchain with other nodes (computers) attached to the blockchains network. |
| 21 | Confirmed | When a transaction has been confirmed, this means it's been approved by the Cryptocurrency's network and permanently appended to the Blockchain. |
| 22 | Decentralized application (dApp, DApp, or Dapp) | A computer application that runs on a Distributed computing system. |
| 23 | Digital currency | A balance or a record stored in a distributed database on the Internet, in an electronic computer database, within digital files or within a stored-value card. Examples of digital currencies include Cryptocurrencies, virtual currencies, central bank digital currencies (CBDC) and e-Cash. Digital currencies exhibit properties similar to other currencies, but do not have a physical form like the banknotes and coins we are currently used to. Source: Wikipedia - Digital currency |
| 24 | Cryptocurrency | Cryptocurrencies are one form of Digital currency. Cryptocurrency (also called "crypto") has no physical form such as banknotes or physical coins do, but instead exists only in digital form on a network and uses encryption techniques to verify the transfer of funds. Once transactions are verified it is stored on a public ledger called a Blockchain. |
| 27 | ERC-20 | ERC-20 stands for Ethereum Request for Comments 20 and is a token standard that implements an API for tokens within Smart Contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. Many crypto projects are ERC-20 tokens before they develop their own blockchain (mainnet). |
| 28 | Mainnet (Mainnet launch) | A blockchain that's fully developed and deployed. Essentially a mainnet is a projects own "live" blockchain that completes the operations of transferring cryptocurrency from senders to recipients. |
| 29 | Testnet | A working prototype for a blockchain project, that is not yet live. |
| 30 | FUD | An acronym for Fear, uncertainty, and doubt. |
| 31 | Halving | A halving (sometimes referred to as "halvening") relates to miners having their block reward halved at predetermined times when cryptocurrency mining. After a halving occurs, the number of coins or tokens that a miner receives for adding new blocks to the blockchain (i.e. reward for mining new blocks) will be cut in half. While there are many Cryptocurrencies that experience a halving, not all do. However, the most discussed halving in the media is that of the Bitcoin block reward halving. |
| 32 | Initial coin offering (ICO) | ICO is an acronym for Initial coin offering. An Initial coin offering (ICO) is a way of raising funds for new Cryptocurrency projects. |
| 33 | Oracle | An oracle connects real world data to a blockchain. |
| 34 | Sharding | Sharding is the process of splitting a network of blockchain nodes into different groups called shards, in order to improve the scalability and performance of a blockchain network. Every shard processes a small proportion of all transactions simultaneously and in parallel with other shards. These microblocks are then merged into one complete block and added to the primary blockchain. As each shard is running in parallel, there are significant performance improvements in the number of transactions per second that can be processed by the network. Scalability has been one of the key issues with public blockchains over the last couple of years however the introduction of sharding allows for almost linear expansion as the size of the network grows (the more nodes in a network, the more shards can be used, and therefore this parallel processing allows more and more transactions per second). Ethereum 2.0 will introduce sharding as part of this upgrade and projects such as Zilliqa (ZIL) offer sharding capabilities for many existing blockchains. |
| 35 | Smart contract | A smart contract is a computer program or a transaction protocol which is intended to automatically execute, control or document legally relevant events and actions according to the terms of a contract or an agreement. The objectives of smart contracts are the reduction of need in trusted intermediators, arbitrators and enforcement costs, fraud losses, as well as the reduction of malicious and accidental exceptions. Source: Wikipedia - Smart contract Smart contracts can define rules, like a regular contract, and automatically enforce them via the computer code. Ethereum is the largest Cryptocurrency (by Market cap) that offers smart contracts. |
| 36 | FOMO | An acronym for Fear of missing out. |
| 37 | Altcoin | Altcoin is a blend of the words "alternative" and "coin", to form the term Altcoin and is a very common term in Cryptocurrency used to indicate an alternative to Bitcoin. Essentially the term Altcoins refers to all other cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin (BTC). |
| 38 | Bitcoin Pizza Day | Bitcoin Pizza Day is the 22nd May each year and represents the first, real-world transaction using Bitcoin when a Jacksonville, Florida programmer, Laszlo Hanyecz, paid 10,000 bitcoins for two pizzas on the 22nd May 2010. At the time, Bitcoin was worth approximately USD 0.003 cents each. So the 10,000 BTC was theoretically worth about US$30. However, just imagine how much this would be worth at today's Bitcoin price! The deal is legendary with the 22nd of May each year now known as Bitcoin Pizza Day. For those interested, here is the original forum post where Laszlo made the offer... https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=137.0 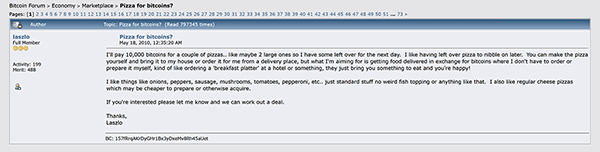 |
| 40 | 51% attack | A 51% attack (also known as a Majority attack or >51% attack) is an attack on a Blockchain network by someone, or a group of miners who collectively control more than 50% of the network's hash rate, in order to fraudulently alter transaction history, reuse coins and halt mining. |
| 41 | Fork (blockchain) | In blockchain, a fork is defined variously as:
Source: Wikipedia - Fork (blockchain) There are two types of Forks that can occur: a Soft fork and a Hard fork. |
| 42 | Gas | Gas is the fee or cost to process a transaction on a blockchain network. |
| 43 | Hodl | Hodl (often written HODL) is one of the original crypto-jargon terms. First said in 2013, Hodl is a slang term in the crypto community for holding a cryptocurrency, rather than selling it. The misspelling of the term "hold" has its origins from a drunken post, with plenty of strong language... that's a warning before clicking the link to read the post in this Bitcoin Forum thread titled I AM HODLING. A person who does this is known as a Hodler. |
| 44 | Peer-to-peer (P2P) | A decentralized approach to interactions between individuals and groups, rather than through an intermediary or central authority. In the case of Cryptocurrency, Peer-to-peer is usually the exchange of digital assets and/or cryptocurrencies via a distributed computing network system. A P2P exchange platform allows buyers & sellers to trade cryptocurrency between each other without the need for intermediaries. |
| 45 | Decentralized finance (DeFi) | Decentralized Finance, or "DeFi" for short, is the concept that traditional financial services (such as financial markets, lending, banking and other investment services) can be recreated and/or improved upon by using decentralized financial infrastructure and applications created on blockchain technology. |
| 46 | Stablecoin | Stablecoins are a type of Cryptocurrency where their value is backed or tied to a relatively more "stable" asset. The aim is to offer greater price stability (less volatility) than cryptocurrencies as a whole currently do by combining the stability of the underlying asset with the efficiency of blockchain technology. A Stablecoin can be pegged to Fiat money (such as AUD, USD, Euro, Yen, etc), to commodities (such as Gold), or even to another Cryptocurrency. Examples include: Tether (USDT); USD Coin (USDC); TrueUSD (TUSD); Dai (DAI); Paxos Standard (PAX); and many more. |
| 47 | Satoshi (unit) | A Satoshi (also called "sat") is the smallest unit of a bitcoin, equivalent to 100 millionth of a bitcoin (8 decimal places). |
| 48 | Satoshi Nakamoto | Satoshi Nakamoto is a Pseudonym (Alias) for the developer/s of Bitcoin. To date, the true identity of this person or group of developers has never been revealed or confirmed. |
| 49 | Protocol | A set of software rules. |
| 50 | MyEtherWallet (MEW) | MyEtherWallet (also known as "MEW") is a non-custodial wallet solution, that allows users to interact with Ethereum based applications (such as Decentralized finance apps) while maintaining custody of their digital assets. MEW COO Brian Norton, has stated this allows users to maintain their own funds while interacting with these different blockchain applications in a trustless, permissionless, and privacy orientated way. MyEtherWallet launched their first web-based crypto wallet in 2015, and have since added full mobile application and browser extension support. |
| 51 | On-chain | The term on-chain has many variations however essentially refers to data that is directly on, or related to, a blockchain (as opposed to "off-chain" which is data which is not related to a blockchain). For example, on-chain transactions refer to transactions that are recorded and verified on the blockchain. On-chain analysis is an emerging field proving credible in valuing and analyzing these new types of digital assets and markets, where conventional financial valuation metrics are insufficient. Glassnode is one of the leading blockchain data and intelligence providers who generates comprehensive on-chain metrics and tools for digital asset holders and investors. |
| 52 | Whales (Cryptocurrency whales) | Cryptocurrency whales refers to individuals or entities (such as hedge funds) that hold significantly large amounts of a particular Cryptocurrency. For example, a Bitcoin whale would be an individual or entity which holds such a large amount of Bitcoin that they could potentially move the market (to manipulate the BTC price) if they were to sell all their holdings at once. |
| 53 | Blockchain domain | A blockchain domain is similar to traditional domains such as .com and .net, except the records are stored on a Blockchain, creating two unique benefits: 1) simplifying crypto payments; and 2) build uncensorable websites. Examples of blockchain domains include .crypto .wallet .nft .blockchain and more. Please refer to the Unstoppable Domains review for a list of available domain names and the full benefits of blockchain domains. |
| Term | Description |
